The following excerpt is from Gut Feelings- Disorders of Gut-Brain Interactions & the Patient/Doctor Relationship, a groundbreaking book on the science, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the gut-brain interaction (DGBI) and the importance of effective communication skills for patients and their doctors.
What are the Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction (DGBI)?
There are 33 adult and 20 pediatric DGBIs in the Rome IV classification that share an underlying definition as a “group of disorders classified by gastrointestinal symptoms related to any combination of”:
- Motility disturbance (abnormal movement inside the bowels)
- Visceral hypersensitivity (more intense abdominal pain than usual in response to stimuli)
- Altered mucosal and immune function (changes to the bowel’s mucous membrane and immune response, e.g., “leaky gut”)
- Altered gut microbiota (changes to the normal microbes found in a healthy gut, e.g., dysbiosis or imbalance of “good” and “bad” bacteria)
- Altered central nervous system (CNS) processing (changes in how the brain processes pain and other GI symptoms).”
Each of the DGBIs is then organized into anatomical domains, as shown in the graphic. In this manner, irritable bowel or functional constipation would be part of the bowel disorders domain, while functional dyspepsia or nausea/vomiting syndrome would belong in the gastroduodenal disorders domain.
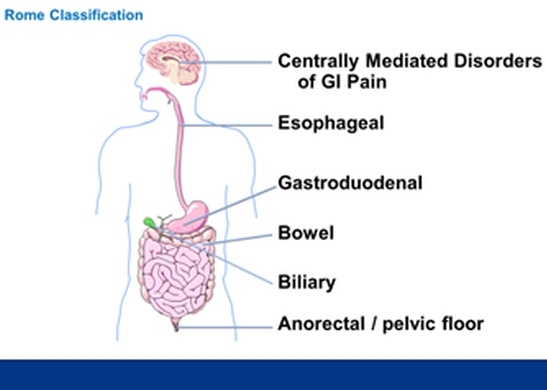
The anatomical basis we use to categorize DGBIs according to the Rome IV classification. This diagram shows the anatomic domains of the GI system that Rome IV uses to organize the DGBIs. Each DGBI diagnosis is placed into one of these domains. Thus, IBS and functional constipation are bowel disorders, and functional dyspepsia or nausea/vomiting syndromes are gastroduodenal disorders.
For complete details about each DGBI, including their definition, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation including Rome IV criteria, and treatments, purchase the book directly from the authors or find it on Amazon.
Commonwealth Diagnostics International (CDI) is a proud corporate partner to the Rome Foundation, DrossmanCare and the Gut Feelings book. Gut Feelings was written as a collaboration by Douglas A. Drossman MD, an internationally acclaimed gastroenterologist and co-founder of the Rome Foundation, and Johannah Ruddy MEd, a patient advocate and current executive director of the Rome Foundation.

